Saving and restoring a RecyclerView's position in Android
When using a RecyclerView in your Android app, especially one with many (or infinite) items inside it, your users will get pretty frustrated if you fail to remember their position.
I recently used a RecyclerView to show a few hundred rows, each of which may link to another fragment, returning from which will reinitialise the fragment. With the default implementation, every time the RecyclerView’s Adapter is assigned the position is reset. In this tutorial, I’ll cover how to save, load, and reset this position.
Note that this tutorial will only work if your RecyclerView’s content / order won’t change. Kotlin is used for this article’s code, but the technique also works in Java. It is also available as a GitHub Gist if you’d like to just see the code.
Prerequisities
Since the position restoring framework will be reused, first create an interface ListPositioner.kt:
interface ListPositioner {
val recyclerScrollKey: String
fun loadListPosition()
fun saveListPosition()
fun resetListPosition()
}
Next, make sure your controller class (Fragment, Activity, etc) implements ListPositioner (e.g. MyFragment : ListPositioner).
Finally, we need a SharedPreferences key to store the scroll position in:
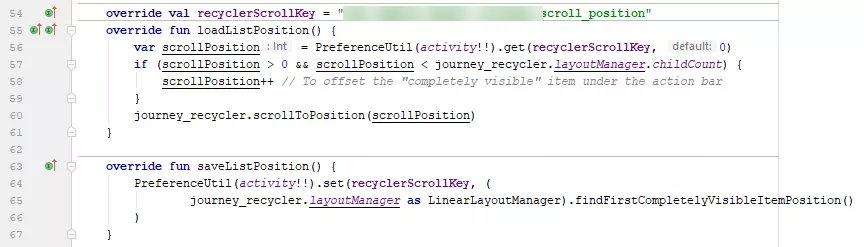
override val recyclerScrollKey = "uk.co.jakelee.scrollposition"
Saving the RecyclerView’s scroll position
To save the position, we’re just going to save the first fully visible item’s position into SharedPreferences. First retrieve the scroll position of your RecyclerView (myRecycler in this example), then save it:
override fun saveListPosition() {
val position = (myRecycler.layoutManager as LinearLayoutManager).findFirstCompletelyVisibleItemPosition()
PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(activity!!)
.edit()
.putInt(recyclerScrollKey, position)
.apply()
}
Note that apply() saves the preference in the background, if you’re going to be rapidly returning to the RecyclerView you may need commit() as it saves immediately. Additionally, you may find .findFirstVisibleItemPosition() works better in your use case as it depends on average row height somewhat.
Loading the RecyclerView’s scroll position
Loading the scroll position is even simpler, as scrollToPosition() is used:
override fun loadListPosition() {
val scrollPosition = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(activity!!).getInt(recyclerScrollKey, 0)
myRecycler.scrollToPosition(scrollPosition)
}
Note that if you are currently drawing your RecyclerView under the toolbar / other views, you may need to (safely) manually adjust the scrollPosition. “Fully visible” actually only refers to “fully visible somewhere”, even if it is under another view! In my case, the adjustment needed was:
override fun loadListPosition() {
var scrollPosition = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(activity!!).getInt(recyclerScrollKey, 0)
if (scrollPosition > 0 && scrollPosition < myRecycler.layoutManager.childCount) {
scrollPosition++ // To offset the "completely visible" item under the action bar
}
myRecycler.scrollToPosition(scrollPosition)
}
Resetting the RecyclerView’s scroll position
Finally, you’ll likely want to regularly reset the scroll position if you change the RecyclerView content, the user logs out, etc. This is done by just resetting the SharedPreference:
override fun resetSavedListPosition(){
PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(activity!!)
.edit()
.putInt(recyclerScrollKey, 0)
.apply()
}
This post is also available as a GitHub Gist.