Generic SharedPreferences Utility Class
Recently, a project required both backed up and non-backed up SharedPreferences, as well as an easy way to read and write these values. The following class was created with this functionality, using generics in Kotlin for practice. This post will walkthrough some of the key features, the finished code is also available as a Gist.
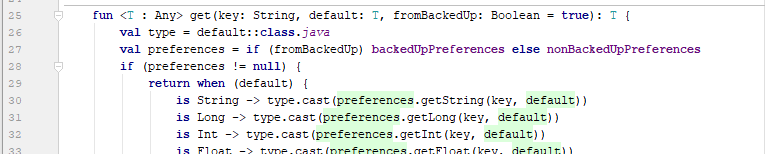
Generic get & set
Most importantly, the datatype to read / write is determined by the default value passed. E.g. if the default datatype is a string, getString will be used. This can be a problem when storing numbers, as passing a long for a value saved as an int will not return the correct SharedPreference.
The result of the SharedPreference setting is returned as a boolean so the caller can have confidence in the save’s success.
fun set(key: String, value: T, toBackedUp: Boolean = true): Boolean {
val preferences = if (toBackedUp) backedUpPreferences else nonBackedUpPreferences
if (preferences != null && !TextUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
val editor = preferences.edit()
when (value) {
is String -> editor.putString(key, value)
is Long -> editor.putLong(key, value)
is Int -> editor.putInt(key, value)
is Float -> editor.putFloat(key, value)
is Boolean -> editor.putBoolean(key, value)
else -> return false
}
return editor.commit()
}
return false
}
Backed up and non-backed up preferences
As some preferences should be backed up (e.g. user choices), and others not (e.g. current app state), there are 2 SharedPreferences files used. By default, all values are read from / written to the backed up file, but this can be overridden by passing false to the get / set function.
private val backedUpPreferences: SharedPreferences?
private val nonBackedUpPreferences: SharedPreferences?
init {
backedUpPreferences = application.getSharedPreferences(BACKED_UP_NAME, MODE_PRIVATE)
nonBackedUpPreferences = application.getSharedPreferences(NON_BACKED_UP_NAME, MODE_PRIVATE)
}
companion object {
private const val BACKED_UP_NAME = "com.yourcompany.BACKED_UP"
private const val NON_BACKED_UP_NAME = "com.yourcompany.NON_BACKED_UP"
}
The backup logic is added via a file called backup_rules.xml, in /src/main/res/xml containing the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<full-backup-content>
<include domain="sharedpref" path="com.yourcompany.BACKED_UP.xml" />
</full-backup-content>
The following should also be added to the AndroidManifest.xml inside the application element:
android:allowBackup="true"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
Legacy support
To ensure that legacy (non-generic) SharedPreferences uses can be easily replaced, get & set wrappers are provided for the 4 major types (string, long, integer, boolean).
fun getStringPreference(key: String, defaultValue: String = ""): String = get(key, defaultValue)
fun getLongPreference(key: String, defaultValue: Long = 0L): Long = get(key, defaultValue)
fun getIntegerPreference(key: String, defaultValue: Int = 0): Int = get(key, defaultValue)
fun getBooleanPreference(key: String, defaultValue: Boolean = false): Boolean = get(key, defaultValue)
fun setStringPreference(key: String, value: String): Boolean = set(key, value)
fun setLongPreference(key: String, value: Long): Boolean = set(key, value)
fun setIntegerPreference(key: String, value: Int): Boolean = set(key, value)
fun setBooleanPreference(key: String, value: Boolean): Boolean = set(key, value)
Possible improvements
Currently, any object can be passed to the getters or setters, not just the 4 supported types. A future improvement would be to only accept values actually supported for storage.
Additionally, a way to enforce certain keys always getting / setting the same type would help prevent hard to track down errors, as would checking both SharedPreferences files for a given key.
All code is available in a Gist.